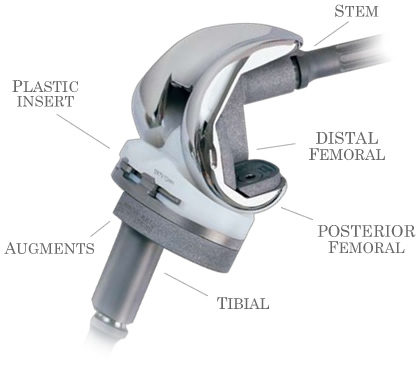
Artificial Knee Components
Augments
A femoral augment, or set of augments, for use with a knee joint prosthesis, where the femoral augment includes a main body portion, an aperture formed within the main body portion and extending in a generally distal/proximal direction, and a pair of legs extending outwardly from said main body portion in a generally posterior direction.
Stems
Stems improve the mechanical stability of tibial components in total knee replacement (TKR), but come at a cost of stress shielding along their length. Their advantages include resistance to shear, reduced tibial lift-off and increased stability by reducing micromotion. Longer stems may have disadvantages including stress shielding along the length of the stem with associated reduction in bone density and a theoretical risk of subsidence and loosening, peri-prosthetic fracture and end-of-stem pain. These features make long stems unattractive in the primary TKR setting, but often desirable in revision surgery with bone loss and instability. In the revision scenario, stems are beneficial in order to convey structural stability to the construct and protect the reconstruction of bony defects.
Patella Component
The patellar component replaces the surface on bottom of the patella. The “top” of the kneecap is the part you can feel through your skin. The “bottom” is the on the other side, and slides up and down in the femoral groove when you bend or straighten your leg.
Plastic Insert & Tibial Base Plate
The tibial component replaces the end of the tibia—commonly called the shinbone. The tibial component is made up of the plastic spacer which provides a weight-bearing surface and the metal tibial tray that is fitted directly onto the bone. The plastic used is very tough and very slick – so slick and tough that you could ice skate on a sheet of the plastic without much damage to the plastic
Femoral Component
The femoral component is metal and replaces the end of the femur, the groove where the kneecap slides. The femur is commonly called the thighbone. It is the largest bone in the body.
Types of knee Prosthesis
Types of metal used
- Cobalt-chromium alloys
- Titanium and titanium-cobalt
Plastic inserts
- XLPE
- UHMWPE
Fixed or mobile bearing
Cemented or uncemented
All poly tibial component
Cruciate retaining or Cruciate sacrificed
Bi-cruciate Knee Prosthesis
Gender Knee Prosthesis
High Flex Knee Prosthesis
UNI Knee Replacement
Patello-femoral Replacement
Constrained or semi-constrained Prosthesis
Primary or Revision Prosthesis
Hinged Knee Prosthesis
Tumor Prosthesis