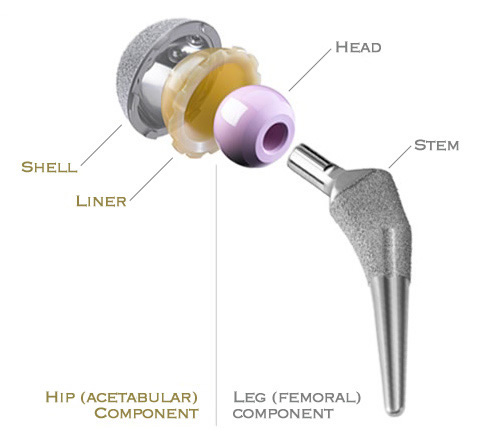
Stem
The stem is fixed into the thigh bone (femur). A cemented stem is held in place by a type of acrylic cement that acts as a grout, filling the bone marrow space between the metal stem and the bone. A cementless prosthesis has a fine mesh, beaded or porous surface which abuts against living bone. Bone grows into these uneven depressions on the surface of the implant. Surface coatings such as hydroxyapatite (HA) may also be applied to the irregular surface of cementless stems.
Head
The head or ball articulates with the liner and can be manufactured from metal or ceramic. The head is inserted on the morse taper at the top of the stem.
Liner
The liner is fixed inside the shell. It acts as a bearing surface for the head or ball which is attached to the stem. Movement causes friction between the lining and the head. Therefore, the materials that form the lining are crucial to reduce wear to a minimum. The articulating surfaces must be exceptionally smooth but also very hard-wearing.
Shell
The shell fits into the hip joint socket and needs to be fixed in place. The materials used for the shell are crucial to enable the implant to be fixed to the hip socket effectively. Shells are made from metal. For the last twenty years cobalt chrome or titanium alloys have been the most popular materials. However, recent advances using porous metals have significantly improved the ability of the bone to grow quickly into the outer surface of the shell. The shells are made from pure titanium or tantalum with pores in the metal that mimic coral. This helps the living bone to grow into the coral-like porous metal. These two materials are highly bio-compatible, but at the same time they are strong and flexible and are ideal for revision hip surgery.
Types of Hip Prostheses
Types of metal used
- Cobalt-chromium alloys
- Titanium and titanium-cobalt
Plastic inserts
- XLPE
- UHMWPE
- ALTRX
Bearing Surfaces
- Metal on metal (MOM)
- Metal on polyethylene (MOP)
- Ceramic on polyethylene (COP)
- Ceramic on ceramic (COC)
- Ceramic on metal (COM)
Types of Hip Prostheses
- Mobile bearing hip (dual mobility) Prosthesis
- Monobloc or Modular Prosthesis
- Fixed bearing hip Prosthesis
- Modular hip Prosthesis
- Cementless (press fit) or cemented Prosthesis
- Primary or revision Prosthesis
- Short stem Prosthesis
- Tissue sparing – bone conserving Prosthesis
- Tumor Prosthesis
- Bipolar Prosthesis
- Moores Prosthesis
- Thompsons Prosthesis
Classification of cementless femoral stems.
- Single wedge
- double wedge
- metaphyseal filling
- Tapered: round, cone & rectangle
- Cylindrical fully coated
- Modular
- Anatomic