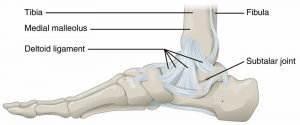
Ankle instability is caused by injury to the lateral [outside] ankle ligaments. This usually causes strain or stretch, and in more severe forms, causes a sprain or tear in the ligaments. This can lead to a sense of instability (giving out) in the ankle and predispose the patient to get frequent ankle sprains even with minor trauma or twist.
Often, patients with ankle instability can be treated without surgery by strengthening the muscles that control the ankle joint, avoiding high-risk activities and using a supportive brace or shoe to decrease the risk of recurrent ankle sprains. In some patients, non-operative treatment is not successful, and surgery is required to either tighten up the ligaments supporting the outside of the ankle, or to reconstruct these ligaments using a tendon graft.