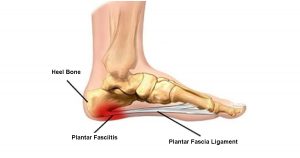
Plantar fasciitis is a disorder of the connective tissue which supports the arch of the foot. It results in pain in the heel and bottom of the foot that is usually most severe with the first steps of the day or following a period of rest. Pain is also frequently brought on by bending the foot and toes up towards the shin. The pain typically comes on gradually, and it affects both feet in about one-third of cases.
The cause of plantar fasciitis is not entirely clear. Risk factors include overuse, such as from long periods of standing, an increase in exercise, and obesity. It is also associated with inward rolling of the foot, a tight Achilles tendon, and a sedentary lifestyle. It is unclear if heel spurs have a role in causing plantar fasciitis even though they are commonly present in people who have the condition.
Plantar fasciitis is a disorder of the insertion site of the ligament on the bone characterized by micro tears, breakdown of collagen, and scarring. Since inflammation plays either a lesser or no role, a review proposed it be renamed plantar fasciosis. The presentation of the symptoms is generally the basis for diagnosis; with ultrasound sometimes being useful if there is uncertainty. Other conditions with similar symptoms include osteoarthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, heel pad syndrome, and reactive arthritis.