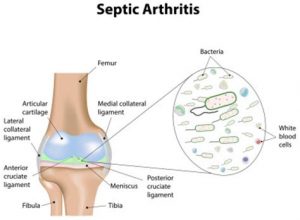
Septic arthritis of the knee, also known as joint infection or infectious arthritis, is the invasion of a joint by an infectious agent resulting in joint inflammation. Symptoms typically include redness, heat and pain in a single joint associated with a decreased ability to move the joint. Onset is usually rapid. Other symptoms may include fever, weakness and headache. Occasionally, more than one joint may be involved.
Causes include bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites.Risk factors include an artificial joint, prior arthritis, diabetes and poor immune function. Most commonly, joints become infected via the blood but may also become infected via trauma or an infection around the joint. Diagnosis is generally based on aspirating joint fluid and culturing it. White blood cells of greater than 50,000 mm3 or lactate greater than 10 mmol/l in the joint fluid also makes the diagnosis likely.
Initial treatment typically includes antibiotics such as vancomycin, ceftriaxone or ceftazidime. Surgery may also be done to clean out the joint. Without early treatment, long-term joint problems may occur. Septic arthritis occurs in about 5 people per 100,000 each year. It occurs more commonly in older people.